2. Shortness of breath
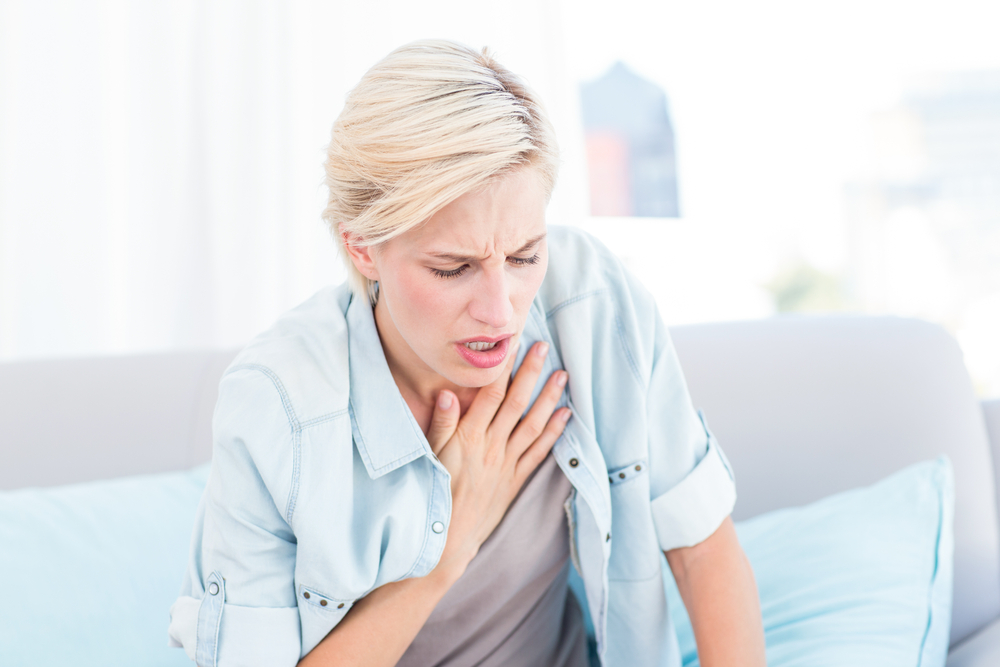

About 70 percent of patients with the disease suffer from pleural mesothelioma. Shortness of breath is one of the most common symptoms, but it is not always constant. The most common reason for the symptom is pleural effusion, which consists of fluid buildup in the space between the two layers of the pleura. Pleural effusions are progressive and they start to occupy the space in the lungs, causing shortness of breath. As the disease progresses, shortness of breath becomes more severe.
In addition, it may be caused by loss of chest wall mobility, a problem related to mesothelioma in the chest wall which makes it less flexible and causes decreased chest movements as a person breathes. Loss of lung volume happens as mesothelioma in the pleura grow into the lung tissue and decrease the lung’s capacity to properly function. Pericardial effusion is also a possibility and it is similar to pleural effusions, but it occurs in the pericardial sac of the heart. Any patient with mesothelioma can suffer from shortness of breath, but it is more common among patients with pleural mesothelioma.