Mesothelioma is an aggressive type of cancer that develops in the cells that line certain organs (particularly in the chest and abdomen), due to asbestos exposure. Most commonly, mesothelioma occurs in the cells that line the lungs, which is known as pleural mesothelioma, but it also occurs in the abdomen, known as peritoneal mesothelioma; the heart, known as pericardial mesothelioma; and testicles, known as testicular mesothelioma. The four different types of mesothelioma are defined according to the part of the body affected.
The mesothelium is the group of cells that line and help protect the organs, by creating a special lubricating fluid that enables movement between the organs. This type of cancer is often diagnosed after a patient seeks a doctor due to the first signs of the disease.
The following symptoms may not be conclusive for a diagnosis, and a physician will need additional tests to confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis. However, these symptoms may include:
1. Dry cough and wheezing
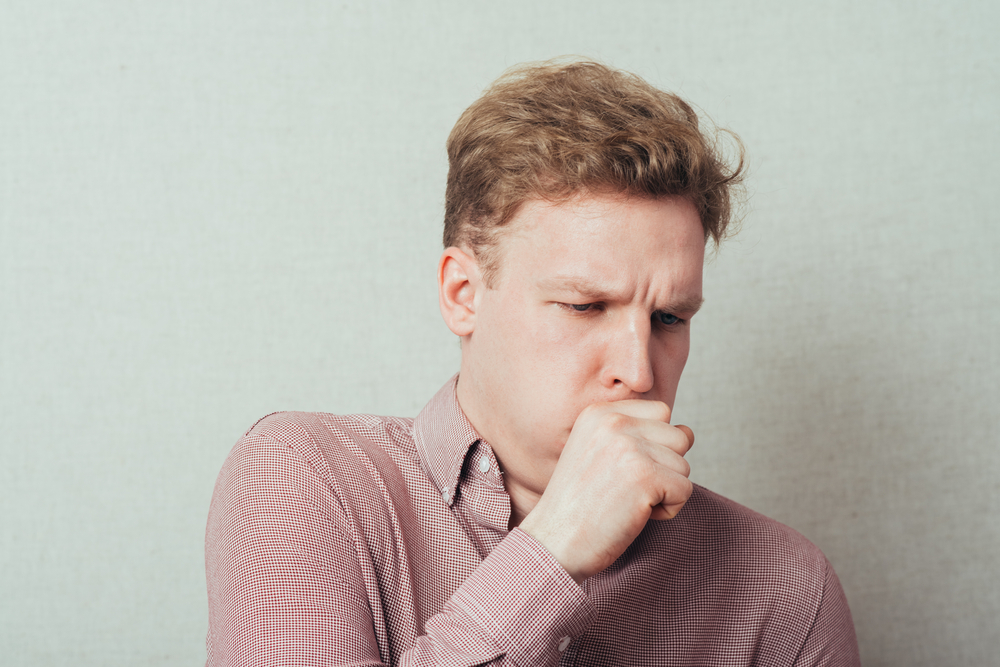

Coughing is the way the body removes foreign material or mucus from the lungs and airways, or the reaction to an irritated airway. While an occasional cough is normal, a persistent cough can indicate an underlying problem. Similarly, wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound people can make while breathing and can indicate a respiratory problem. In the case of mesothelioma, it is more common among patients who suffer from pleural mesothelioma. In the early stages of the disease, the symptoms are mild, including persistent coughing and/or wheezing and may be mistaken for other lung diseases.
However, in late stages of pleural mesothelioma, the symptoms become more specific and severe, including persistent coughing together with coughing up blood (hemoptysis) and wheezing.